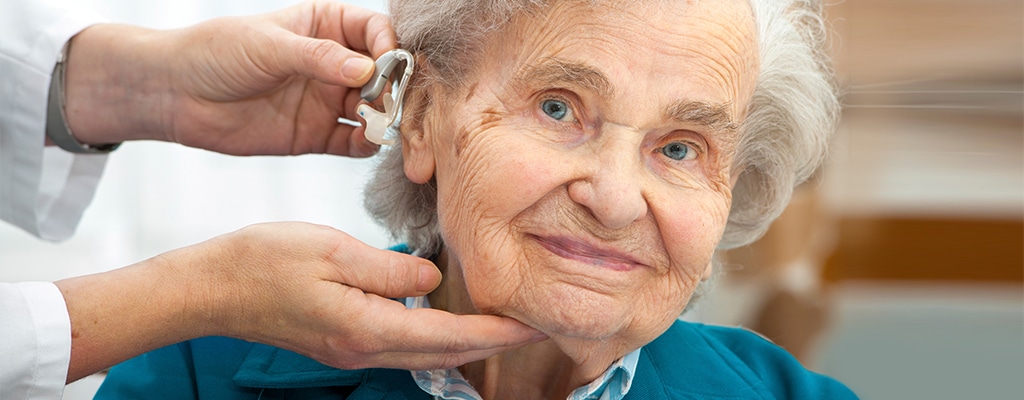

Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is a partial or total inability to hear. It can occur in one or both ears and can range from mild to profound. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent and can affect people of all ages. There are various causes of hearing loss, including genetics, aging, exposure to loud noise, infections, diseases, and trauma to the ear. It can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, communication abilities, and social interactions. Treatment options for hearing loss depend on its cause and severity and may include hearing aids, cochlear implants, assistive listening devices, and in some cases, medical or surgical interventions.
Hearing loss is a prevalent condition with far-reaching implications, impacting communication, relationships, and overall quality of life. Recognizing the urgency of early detection and intervention is paramount in effectively managing this challenge.
Early detection enables prompt intervention, preventing further deterioration and enhancing treatment outcomes. Routine screenings are essential, especially for high-risk groups such as older adults and individuals exposed to loud noise.

Additionally, there are various causes of hearing loss, including genetic factors, aging (presbycusis), prolonged exposure to loud noises (noise-induced hearing loss), infections such as otitis media or meningitis, traumatic injury to the ear, and certain medical conditions like Meniere’s disease or autoimmune disorders. Understanding the type and cause of hearing loss is essential for determining the most appropriate treatment and management strategies.

Hearing loss can manifest through various symptoms, which may vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
Experiencing any of these symptoms may indicate the presence of hearing loss and should prompt further evaluation by a healthcare professional, such as an audiologist or otolaryngologist. Early detection and intervention can help manage hearing loss effectively and improve overall quality of life.
Preventing hearing loss involves adopting proactive measures to protect your ears from damage and preserve your auditory health. Here are some essential strategies:
Limit exposure to loud noises: Avoid prolonged exposure to loud environments or use ear protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, when exposed to loud sounds at work, concerts, or sporting events.
Turn down the volume: When listening to music or watching TV or movies, keep the volume at a moderate level to prevent damage to your ears over time.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of hearing loss and maintain optimal auditory health throughout your life.
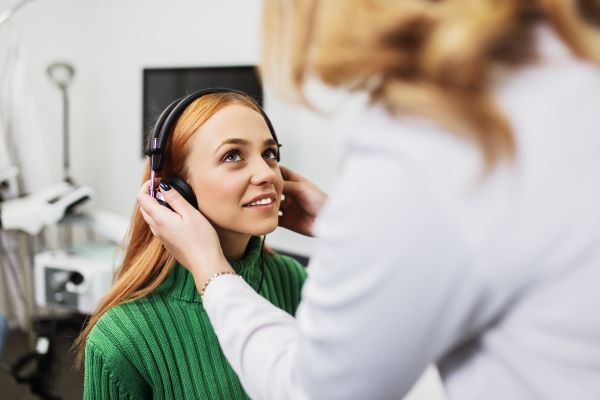

Treatment for hearing loss depends on the type, severity, and underlying cause of the condition. Here are some common treatment options:
Hearing aids: These devices amplify sound and improve hearing for individuals with mild to severe hearing loss. They come in various styles and can be customized to suit individual needs.
Cochlear implants: Suitable for individuals with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss, cochlear implants bypass damaged parts of the inner ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, allowing for improved hearing.
Treatment options are tailored to each individual’s specific needs and may involve a combination of approaches to effectively manage hearing loss and improve quality of life. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an audiologist or otolaryngologist, to determine the most suitable treatment plan.